Arteriogenesis: the key to success
For patients who are surgical candidates, the solution to their arterial obstruction comes as quickly as a surgeon can work.
However, this means that non-operable patients and their doctors are left to find alternative solutions to improving lower extremity circulation. Drugs and lifestyle changes may work as long as the regimen is maintained, but these may still present problems according to each patient’s case.
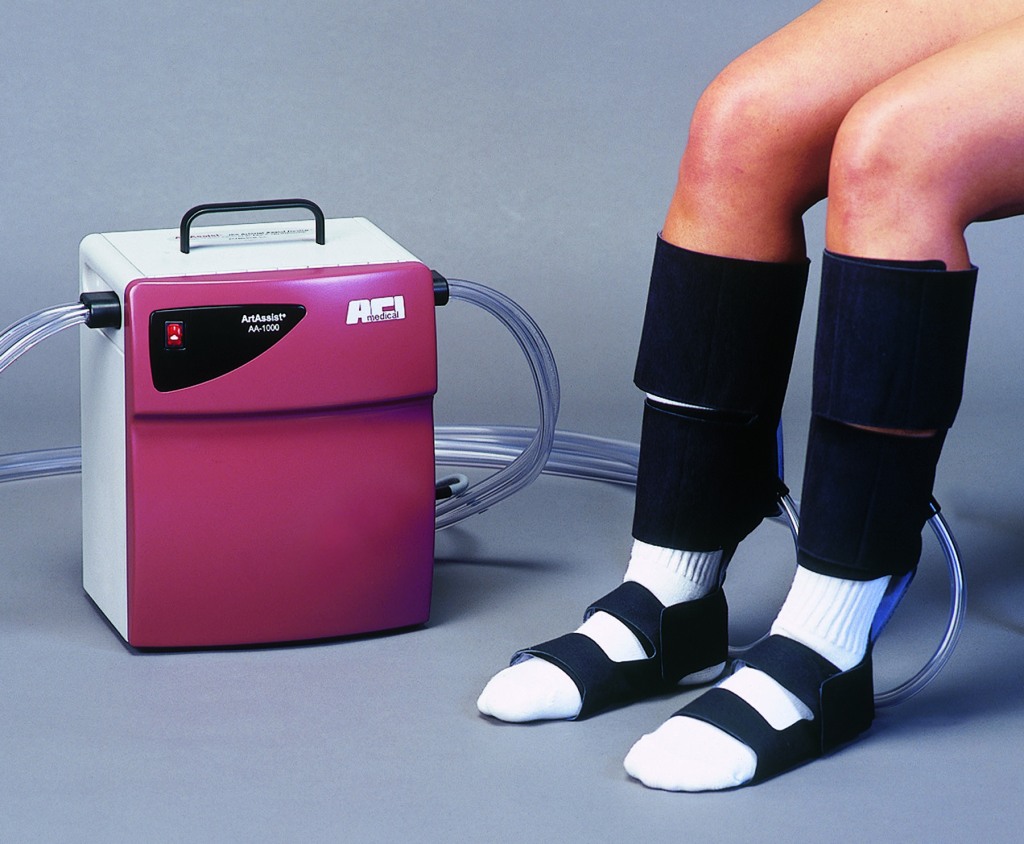
Patients who use the ArtAssist® device every day for at least 90 days have developed permanent collateral arteries as a result of therapy.
This solution may be ideal for doctors with patients who have otherwise run out of options. With proven efficacy and consistently high success rates, those with severe PAD get another chance to rebuild and strengthen the collateral arteries in their lower extremities.
The theory
When developers optimized the ArtAssist® device to maximize blood flow to the lower extremities, they realized that, even after having stopped therapy with the device, patients kept their improved circulation. “Why is this?” they asked.
 After some educated guessing, Paul van Bemmelen, MD, PhD of Temple University began looking into the hypothesis more closely. This publication (Fig. 1) is the first to have documented a threatened limb before and after four months of ArtAssist® device therapy.
After some educated guessing, Paul van Bemmelen, MD, PhD of Temple University began looking into the hypothesis more closely. This publication (Fig. 1) is the first to have documented a threatened limb before and after four months of ArtAssist® device therapy.
The Rabbit study
In 2007, Dr. van Bemmelen performed another study, this time with a rabbit model. He and his team were able to confirm that intermittent pneumatic compression on the experimental limbs increased the number of angiographical collateral arteries.
How it works
Arteriogenesis, the growth of collateral arteries, can be achieved with a regimen of intermittent pneumatic compression, as we’ve just seen. But what actually happens inside the vessels?
Rapid compression causes shear stress on the endothelial cells. These cells react by releasing nitric oxide (NO), which acts as a vasodilator, and tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), which acts as an anticoagulant. These two substances ease the path of nutrient-rich blood through the collateral arteries.
Within a month, patients with peripheral arterial disease (PAD) typically begin to see a dramatic increase in arterial blood flow if they use the ArtAssist® device every day.
After about 90 days, the benefits can be visualized in an arteriogram, as seen above. After this point, a patient may be able to discontinue ArtAssist® device therapy.
Obtaining therapy
Both physicians and patients can contact ACI Medical for information and ordering: toll free (888) 453-4356 or info@acimedical.com
More detailed information can be found at acimedical.com/artassist/order.
References
Angiographic Improvement After Rapid Intermittent Compression Treatment (ArtAssist®) for Small Vessel Obstruction
van Bemmelen, P.; Char, D.; Giron, F; and Ricotta, J.J. Department of Surgery, Division of Vascular Surgery, State University of New York and Stony Brook, NY, USA. Ann Vasc Surg 2003;17:224-228
Long-term Intermittent Compression Increases Arteriographic Collaterals in a Rabbit Model of Femoral Artery Occlusion
van Bemmelen, P.S.; Choudry, R.G.; Salvatore, M.D.; Goldenberg, B.I.; and Blebea, J. Departments for Surgery, and Pathology, Temple University, Philadelphia, USA.
Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 34, 340-346 (2007)